- Have any questions?
- +91 90084 82284
- info@drsridharpsoncologist.com
Bladder Cancer Recurrence After 3 Months
Basal Cell Carcinoma Untreated For 5 Years
July 25, 2024
Stage 2 Wilms Cancer
August 9, 2024Bladder cancer can significantly impact a person’s physical, emotional, and financial well-being. The initial diagnosis and treatment can be exhausting, and the fear of recurrence can add a layer of stress and anxiety.
Dr. Sridhar PS, a trusted name in Cyberknife treatment in India, says:
“A cancer recurrence is a critical concern for patients undergoing initial treatment. Experiencing a recurrence after believing the worst is over can cause profound despair and uncertainty. Bladder cancer recurrence after 3 months is not uncommon and requires vigilant monitoring and proactive treatment.”
In this blog, Dr. Sridhar PS, a renowned Cyberknife specialist in India, addresses the complexities and challenges associated with this condition. Understanding the signs, recurrence rates, and treatment options is essential for improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Are you experiencing bladder cancer recurrence after 3 months? Pleaseconsult a cancer specialist for support and guidance.
Wondering what to watch out for? Let’s dive into the common symptoms.
What are the signs that bladder cancer has returned?
Here are some common signs indicating a bladder cancer return.
- The reappearance of blood in the urine
- Experiencing pain or a burning sensation during urination
- An urge to urinate more often than usual
- Persistent pain in the lower back and pelvic area
- Losing weight without trying
- Swelling or fluid buildup in the legs
- Feeling unusually tired or weak as the body diverts energy to fight the disease
Curious about how often bladder cancer comes back? Here’s what you need to know.
Rate of bladder cancer recurrence after 3 months
The chances of bladder cancer returning are relatively high, even shortly after treatment. Studies indicate that up to 50% of patients might experience recurrence within 1 year.
Dr. Sridhar PS, a sought-after specialist for Cyberknife treatment in India, highlights:
“Patients should undergo frequent cystoscopies, where the doctor visually inspects the inside of the bladder using a scope. Timely follow-up examinations are paramount to swiftly identifying any signs of recurrence. A proactive approach and early intervention can significantly improve prognosis and patient outcomes.”
Dr. Sridhar specializes in advanced techniques for recurrent bladder cancer treatment, ensuring comprehensive care and improved patient outcomes.
Are you worried about the possibility of bladder cancer returning after three months? Please discuss your health history and lifestyle with a cancer specialist for personalized strategies to minimize your risk.
Concerned about the survival rates? Let’s explore the statistics.
Bladder cancer recurrence survival rate
Patients in good health with robust immune systems typically respond better to aggressive treatments necessary for managing the cancer. Advances in medical technology and treatment options continue to improve survival rates for recurrent bladder cancer.
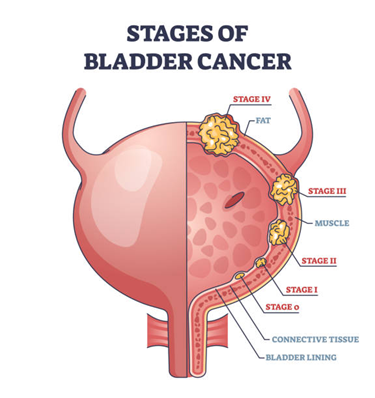
Here are some general statistics to consider:
Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer (NMIBC): Approximately 50-70% of NMIBC cases recur, but only about 10-20% progress to a more advanced stage. The 5-year survival rate for NMIBC patients is generally high, over 90%.
Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer (MIBC): If bladder cancer reaches the muscle-invasive stage, it is more likely to spread and is more lethal. The 5-year survival rate for MIBC can vary widely, from 5% to about 70%, depending on whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body (metastasis) and the effectiveness of the treatment.
Metastatic Bladder Cancer: Once bladder cancer has metastasized, the survival rates decrease significantly. The 5-year survival rate for metastatic bladder cancer is around 5%.
Looking for ways to reduce your risk? Discover effective prevention methods.
How to prevent bladder cancer recurrence?

To prevent bladder cancer recurrence, you can take several proactive steps:
- Attend all follow-up appointments and undergo recommended cystoscopies to monitor for signs of recurrence.
- Stop smoking tobacco, as it significantly increases the risk of bladder cancer returning.
- Eat a diet rich in fruits and vegetables to boost your immune system.
- Drink plenty of fluids, especially water, to help flush out potential carcinogens from the bladder.
- Minimize your exposure to chemicals known to cause bladder cancer, especially in occupational settings.
- Engage in regular physical activity to maintain overall health and enhance immune function.
Need to know the available treatments? Let’s review your options.
Treatment options for recurrent bladder cancer
Treatment options for recurrent bladder cancer vary based on the recurrence’s location and extent, the patient’s previous treatments, and their overall health. Here are the primary treatment approaches:
Surgery:
This involves removing any new tumors that have developed. Depending on the severity, it might range from TURBT (Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor) to more extensive procedures like Cystectomy.
Intravesical therapy:

This treatment involves placing a liquid drug directly into the bladder through a catheter. It’s primarily used for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer to help reduce the risk of recurrence and progression.
Chemotherapy:
Systemic chemotherapy helps kill cancer cells throughout the body for muscle-invasive or advanced recurrent bladder cancer. It may be used before surgery to shrink tumors or eliminate remaining cancer cells post-surgery.
Immunotherapy:
Immunotherapy utilizes the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Agents like checkpoint inhibitors are options for advanced or recurrent bladder cancer that has not responded to other treatments.
Targeted therapy:
These drugs target specific pathways or mutations in cancer cells. They offer a personalized approach to treatment based on the patient’s unique cancer profile.
Radiation therapy:
Often used in combination with chemotherapy, especially for patients who are not candidates for surgery. Radiation can target and destroy cancer cells in specific areas.
Palliative Care:
Focuses on providing relief from symptoms and improving quality of life. This may be appropriate for managing symptoms in advanced, recurrent cases where curative treatment is not possible.
Are you seeking treatment for recurrent bladder cancer? Please connect with an experienced team to explore your treatment options with confidence.
Conclusion
Bladder cancer recurrence after 3 months requires proactive management. Dr. Sridhar PS, a seasoned Cyberknife specialist, stresses early detection and intervention to improve survival rates and quality of life. He encourages patients to maintain regular follow-ups and adhere to prescribed treatments to prevent recurrence and manage their health effectively.
Would you like to undergo effective management and improved quality of life? Please visit a certified cancer doctor to help navigate your options and find the right path forward.
FAQ
What causes bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer typically develops when cells in the bladder begin to grow uncontrollably, often triggered by factors such as prolonged exposure to tobacco smoke and certain industrial chemicals.
Can a CT scan detect bladder cancer?
Yes, a CT scan can help detect bladder cancer by providing detailed images that allow doctors to see unusual growths or abnormalities in the bladder.
Does smoking cause bladder cancer?
Smoking is a major risk factor for bladder cancer, significantly increasing the chance of developing the disease due to harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke that accumulate in the urine.
Can a bladder tumor be non-cancerous?
Not all bladder tumors are cancerous; some are benign, meaning they are non-cancerous and do not spread to other body parts.
Reference Links:
https://www.texasoncology.com/types-of-cancer/bladder-cancer/recurrent-bladder-cancer
